Nacos with Dubbo fusion become registry
Nacos as Dubbo ecosystems important registry implementation, including dubbo-registry-nacos is Dubbo fusion Nacos registry implementation.
Preparatory work
When you put dubbo-registry-nacos integrated into your dubbo project before, please make sure the background nacos service has started. If you are still not familiar with the basic use of Nacos, reference Quick Start for Nacos.
Quick Start
Nacos Dubbo fusion become registry procedure is very simple, general steps can be divided into "increasing Maven dependency" and "the registry".
Increasing Maven dependency
First, you need to dubbo-registry-nacosMaven dependent on added to your project pom.xml file, and strongly recommend that you use the dubbo 2.6.5:
<dependencies>
...
<!-- Dubbo dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Dubbo Nacos registry dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-registry-nacos</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Alibaba Spring Context extension -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>1.0.11</version>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
When a project to adddubbo-registry-nacos, you don't need to explicitly logic programming to realize service discovery and registration, actual implementation is provided by the third party and then configure Naocs registry.
Configuration registry
Suppose you Dubbo application using the Spring Framework assembly, there will be two kinds of optional configuration method, respectively: Dubbo Spring externalized configuration, and the Spring XML configuration files, and, I strongly recommend the former.
Dubbo Spring externalized configuration
Dubbo Spring externalized configuration consists of Dubbo 2.5.8 introduced new features, through the Spring Environment attribute automatically generate and bind the Dubbo configuration Bean, implement configuration to simplify, and lower the threshold of service development.
Suppose you Dubbo applications using Nacos as registry, and the server IP address is:10.20.153.10 at the same time, the registered address as Dubbo externalized configuration properties are stored in dubbo-config.properties file, as shown below:
## application
dubbo.application.name = your-dubbo-application
## Nacos registry address
dubbo.registry.address = nacos://10.20.153.10:8848
##If you want to use your own namespace, you can use the following two methods:
#dubbo.registry.address = nacos://10.20.153.10:8848?namespace=5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932
#dubbo.registry.parameters.namespace=5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932
...
Then, restart your application Dubbo, Dubbo information services and consumption in Nacos console can show:
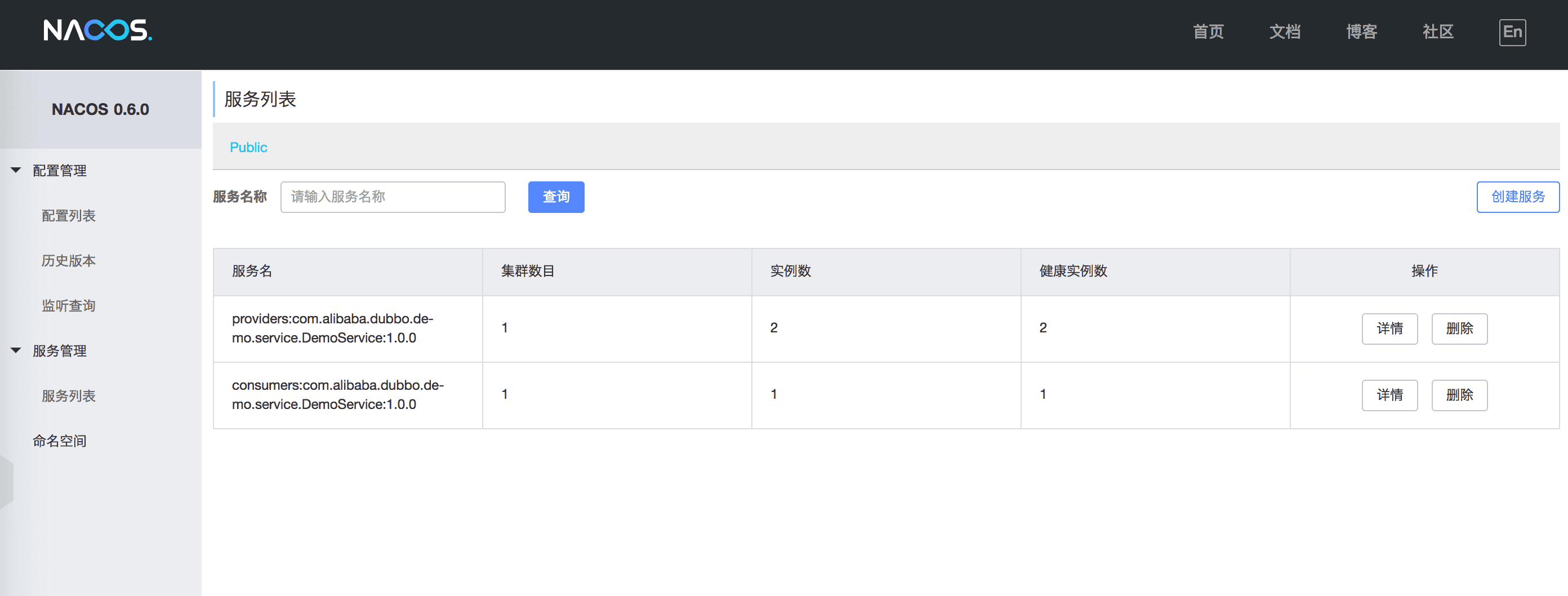
As shown, the service name prefix for providers: metainfo for the service provider's information, consumers: represents the service consumer metainfo. Click"details" can check the service status details:
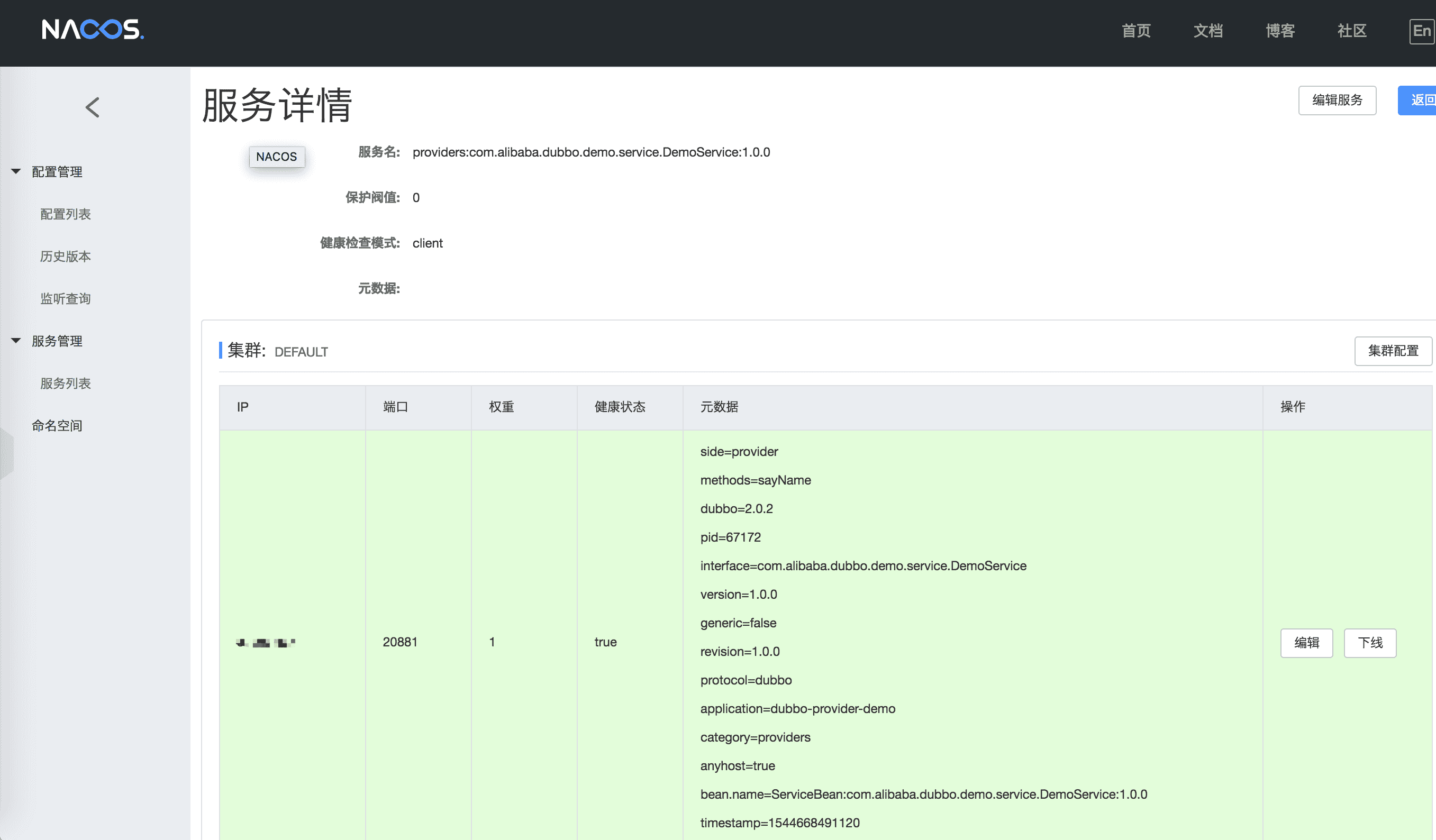
If you are using a Spring XML configuration file assembly Dubbo registry, please refer to the next section.
Spring XML configuration files
Similarly, suppose you Dubbo applications using Nacos as registry, and the server IP address is:10.20.153.10, and assembling Spring Bean in the XML file, as shown below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- 提供方应用信息,用于计算依赖关系 -->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-provider-xml-demo" />
<!-- 使用 Nacos 注册中心 -->
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://10.20.153.10:8848" />
<!-- If you want to use your own namespace, you can use the following configuration -->
<!-- <dubbo:registry address="nacos://10.20.153.10:8848?namespace=5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932" /> -->
...
</beans>
After restart the Dubbo application, you can also find the provider and consumer registered metainfo is presented in Nacos console:
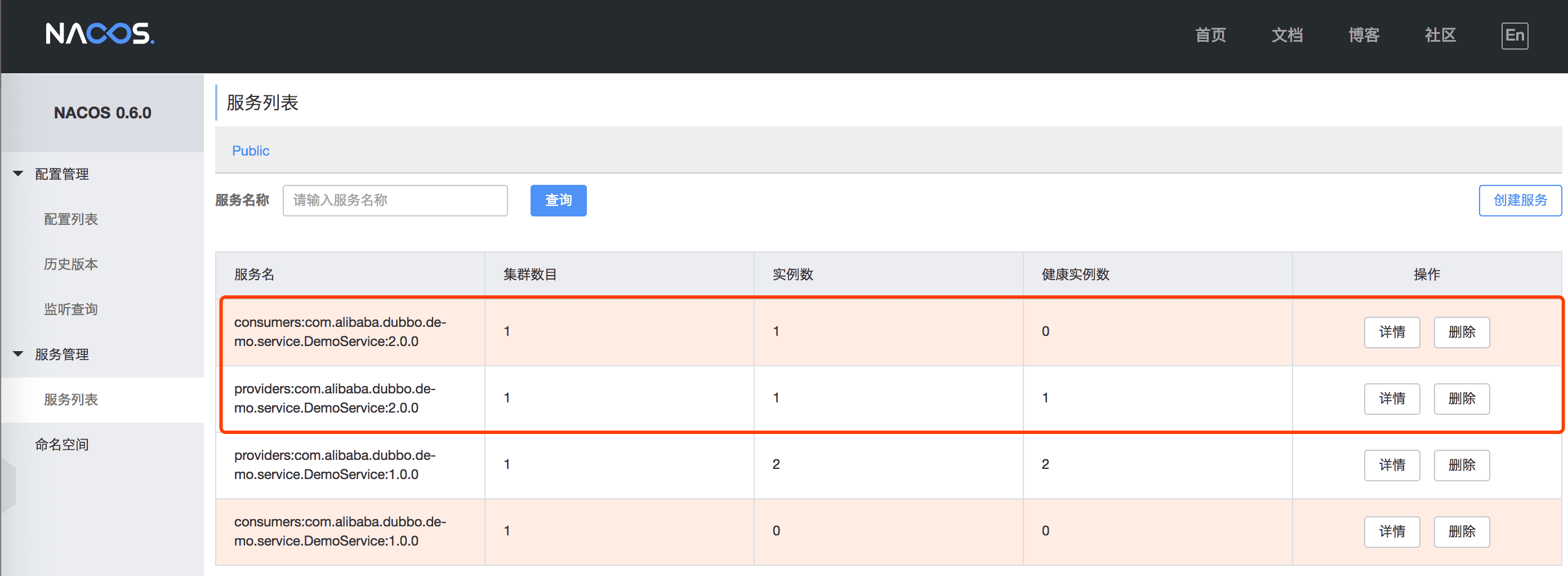
Whether you absolute configuration or switch Nacos registry super Easy? If you are still wanting more or less understand, may refer to the following the complete example.
Complete sample
Above pictures of metadata from Dubbo Spring annotations driver sample and Dubbo Spring XML configuration driven example, the following will introduce both, you can choose your preference programming model.Before the formal discussion, first to introduce the preparation work, because they are dependent on the Java service interface and implementation.At the same time, please make sure that the local (127.0.0.1) environment has launched Nacos service.
Sample interface and implementation
First define the sample interface, as shown below:
package com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.service;
public interface DemoService {
String sayName(String name);
}
Provide the above interface implementation class:
package com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.service;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Service;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcContext;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
/**
* Default {@link DemoService}
* https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/use-nacos-with-dubbo.html
* @since 2.6.5
*/
@Service(version = "${demo.service.version}")
public class DefaultService implements DemoService {
@Value("${demo.service.name}")
private String serviceName;
public String sayName(String name) {
RpcContext rpcContext = RpcContext.getContext();
return String.format("Service [name :%s , port : %d] %s(\"%s\") : Hello,%s",
serviceName,
rpcContext.getLocalPort(),
rpcContext.getMethodName(),
name,
name);
}
}
Interface and implementation after ready, the following will be driven by annotations and XML configuration driven their implementation.
Spring annotations driver sample
https://github.com/nacos-group/nacos-examples/tree/master/nacos-dubbo-example
Dubbo 2.5.7 reconstructed the Spring annotations driver programming model.
Provider annotation driven implementation
- Definition of Dubbo provider externalized configuration properties -
provider-config.properties
## application
dubbo.application.name = dubbo-provider-demo
## Nacos registry address
dubbo.registry.address = nacos://127.0.0.1:8848
##If you want to use your own namespace, you can use the following two methods:
#dubbo.registry.address = nacos://127.0.0.1:8848?namespace=5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932
#dubbo.registry.parameters.namespace=5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932
## Dubbo Protocol
dubbo.protocol.name = dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port = -1
# Provider @Service version
demo.service.version=1.0.0
demo.service.name = demoService
dubbo.application.qosEnable=false
- Implement the provider to guide class -
DemoServiceProviderBootstrap
package com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.provider;
import com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.service.DemoService;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.context.annotation.EnableDubbo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} provider demo
* https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/use-nacos-with-dubbo.html
*/
@EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.service")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/provider-config.properties")
public class DemoServiceProviderBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(DemoServiceProviderBootstrap.class);
context.refresh();
System.out.println("DemoService provider is starting...");
System.in.read();
}
}
The annotation @EnableDubbo activation Dubbo annotation driven and externalized configuration, its scanBasePackages properties scanning to specify the Java package, all marked @Service Service interface implementation class exposure for Spring Bean, then be exported Dubbo Service.
@PropertySource is Spring Framework 3.1 introduced the standard import properties annotation configuration resources, it will provide Dubbo externalized configuration.
Service consumer comments drive implementation
- Definition of Dubbo consumer externalized configuration properties -
consumer-config.properties
## Dubbo Application info
dubbo.application.name = dubbo-consumer-demo
## Nacos registry address
dubbo.registry.address = nacos://127.0.0.1:8848
##If you want to use your own namespace, you can use the following two methods:
#dubbo.registry.address = nacos://127.0.0.1:8848?namespace=5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932
#dubbo.registry.parameters.namespace=5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932
# @Reference version
demo.service.version= 1.0.0
dubbo.application.qosEnable=false
Similarly, dubbo.registry.address attribute points to Nacos registry, other dubbo service relevant meta information through Nacos registry access.
- Implementation services consumer guide -
DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap
package com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.consumer;
import com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.service.DemoService;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.context.annotation.EnableDubbo;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.DubboReference;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} consumer demo
* https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/use-nacos-with-dubbo.html
*/
@EnableDubbo
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/consumer-config.properties")
public class DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap {
@DubboReference(version = "${demo.service.version}")
private DemoService demoService;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(demoService.sayName("Nacos"));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap.class);
context.refresh();
context.close();
}
}
Similarly, @EnableDubbo annotations to activate Dubbo annotation driven and externalized configuration, but the current belong to the Service consumers, without having to specify the Java package name scan label @Service Service implementation.
@Reference is Dubbo remote service dependency injection annotations, need service providers and consumers agreed interface (interface), version (version) and group (group) information.Example, in the current service consumption DemoService service version from the configuration properties file consumer-config.properties.
@PostConstruct code shows when DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap Bean initialization, execution Dubbo ten times remote method invocation.
Run annotation driver sample
Twice in the local boot DemoServiceProviderBootstrap, the registry will appear two health services:

Run again DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap, run results as follows:
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Operate, and service consumer using the load balancing strategy, RPC calls ten times the average contribution to two Dubbo provider instance.
Spring XML configuration driver sample
The Spring XML configuration driven programming model is a traditional Spring assembly components.
Provider XML configuration
- Define the service provider XML context configuration file -
/META-INF/spring/dubbo-provider-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- 提供方应用信息,用于计算依赖关系 -->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-provider-xml-demo"/>
<!-- 使用 Nacos 注册中心 -->
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848"/>
<!-- If you want to use your own namespace, you can use the following configuration -->
<!-- <dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848?namespace=5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932" /> -->
<!-- 用dubbo协议在随机端口暴露服务 -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="-1"/>
<!-- 声明需要暴露的服务接口 -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.service.DemoService" ref="demoService" version="2.0.0"/>
<!-- 和本地bean一样实现服务 -->
<bean id="demoService" class="com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.service.DefaultService"/>
</beans>
- Implement the provider to guide class -
DemoServiceProviderXmlBootstrap
package com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.provider;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} provider demo XML bootstrap
*/
public class DemoServiceProviderXmlBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
context.setConfigLocation("/META-INF/spring/dubbo-provider-context.xml");
context.refresh();
System.out.println("DemoService provider (XML) is starting...");
System.in.read();
}
}
Service consumer driven XML configuration
- Define the service consumer context XML configuration files -
/META-INF/spring/dubbo-consumer-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- 提供方应用信息,用于计算依赖关系 -->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-consumer-xml-demo"/>
<!-- 使用 Nacos 注册中心 -->
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848"/>
<!-- If you want to use your own namespace, you can use the following configuration -->
<!-- <dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848?namespace=5cbb70a5-xxx-xxx-xxx-d43479ae0932" /> -->
<!-- 引用服务接口 -->
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.service.DemoService" version="2.0.0"/>
</beans>
- Implementation services consumer guide -
DemoServiceConsumerXmlBootstrap
package com.alibaba.nacos.example.dubbo.consumer;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} consumer demo XML bootstrap
*/
public class DemoServiceConsumerXmlBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
context.setConfigLocation("/META-INF/spring/dubbo-consumer-context.xml");
context.refresh();
System.out.println("DemoService consumer (XML) is starting...");
DemoService demoService = context.getBean("demoService", DemoService.class);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(demoService.sayName("Nacos"));
}
context.close();
}
}
Run the XML configuration driven example
Similarly, to start the first two DemoServiceProviderXmlBootstrap bootstrap class, observe Nacos registry service provider changes:

XML configuration driven service version for 2.0.0, therefore the registration service and correct.
Again run service consumers leading class DemoServiceConsumerXmlBootstrap, watch the console output:
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("Nacos") : Hello,Nacos
Results also runs and load balancing is normal, but because the current sample has yet to add attributes demo.service.name of therefore, "name" part of the information output null.
If your attention or love Dubbo and Nacos open source project, as well as for their points of "star", related links:
- Apache Dubbo:https://github.com/apache/dubbo
- Dubbo Nacos Registry:https://github.com/apache/dubbo/tree/master/dubbo-registry/dubbo-registry-nacos
- Alibaba Nacos:https://github.com/alibaba/nacos