Kubernetes Nacos
This project contains a Nacos Docker image meant to facilitate the deployment of Nacos on Kubernetes via StatefulSets.
Quick Start
- Clone Project
git clone https://github.com/nacos-group/nacos-k8s.git- Simple Start
If you want to start Nacos without NFS, but emptyDirs will possibly result in a loss of data. as follows:
cd nacos-k8schmod +x quick-startup.sh./quick-startup.sh-
Testing
- Service registration
Terminal window curl -X POST 'http://cluster-ip:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=nacos.naming.serviceName&ip=20.18.7.10&port=8080'- Service discovery
Terminal window curl -X GET 'http://cluster-ip:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=nacos.naming.serviceName'- Publish config
Terminal window curl -X POST "http://cluster-ip:8848/nacos/v1/cs/configs?dataId=nacos.cfg.dataId&group=test&content=helloWorld"- Get config
Terminal window curl -X GET "http://cluster-ip:8848/nacos/v1/cs/configs?dataId=nacos.cfg.dataId&group=test"
Advanced
In advanced use, the cluster is automatically scaled and data is persisted, but PersistentVolumeClaims must be deployed. In this example, NFS is used.
Deploy NFS
- Create Role
kubectl create -f deploy/nfs/rbac.yamlIf your K8S namespace is not default, execute the following script before creating RBAC
# Set the subject of the RBAC objects to the current namespace where the provisioner is being deployed$ NS=$(kubectl config get-contexts|grep -e "^\*" |awk '{print $5}')$ NAMESPACE=${NS:-default}$ sed -i'' "s/namespace:.*/namespace: $NAMESPACE/g" ./deploy/nfs/rbac.yaml- Create
ServiceAccountAnd deployNFS-Client Provisioner
kubectl create -f deploy/nfs/deployment.yaml- Create NFS StorageClass
kubectl create -f deploy/nfs/class.yaml- Verify that NFS is working
kubectl get pod -l app=nfs-client-provisionerDeploy database
- Deploy master
cd nacos-k8s
kubectl create -f deploy/mysql/mysql-master-nfs.yaml- Deploy slave
cd nacos-k8s
kubectl create -f deploy/mysql/mysql-slave-nfs.yaml- Verify that Database is working
# masterkubectl get podNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEmysql-master-gf2vd 1/1 Running 0 111m
# slavekubectl get podmysql-slave-kf9cb 1/1 Running 0 110mDeploy Nacos
- Modify deploy/nacos/nacos-pvc-nfs.yaml
data: mysql.master.db.name: "db name" mysql.master.port: "master db port" mysql.slave.port: "slave db port" mysql.master.user: "master db username" mysql.master.password: "master db password"- Create Nacos
kubectl create -f nacos-k8s/deploy/nacos/nacos-pvc-nfs.yaml- Verify that Nacos is working
kubectl get pod -l app=nacos
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEnacos-0 1/1 Running 0 19hnacos-1 1/1 Running 0 19hnacos-2 1/1 Running 0 19hScale Testing
- Use
kubectl execto get the cluster config of the Pods in thenacosStatefulSet.
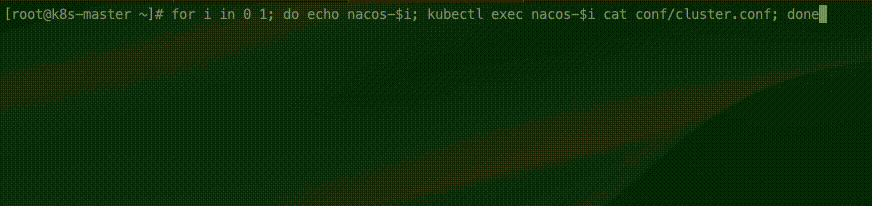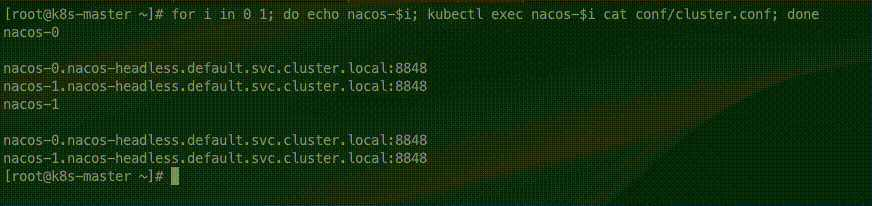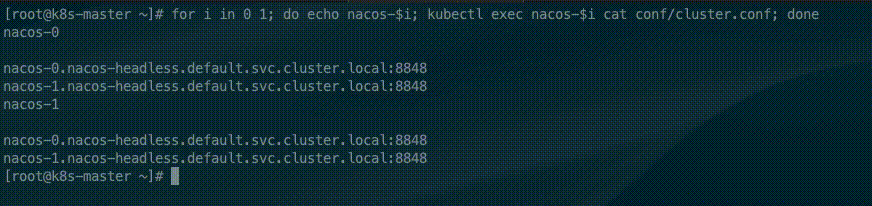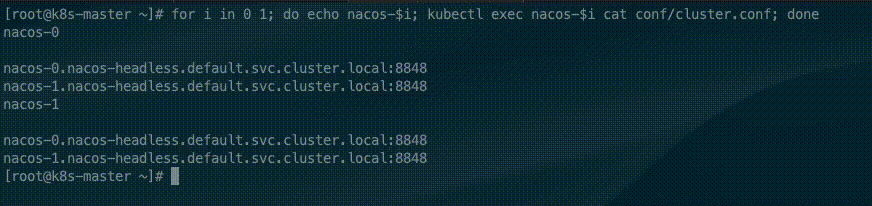
for i in 0 1; do echo nacos-$i; kubectl exec nacos-$i cat conf/cluster.conf; doneThe StatefulSet controller provides each Pod with a unique hostname based on its ordinal index. The hostnames take the form of <statefulset name>-<ordinal index>. Because the replicas field of the nacos StatefulSet is set to 2, In the cluster file only two nacos address
- Use kubectl to scale StatefulSets
kubectl scale sts nacos --replicas=3
- Use
kubectl execto get the cluster config of the Pods in thenacosStatefulSet after scale StatefulSets
for i in 0 1 2; do echo nacos-$i; kubectl exec nacos-$i cat conf/cluster.conf; done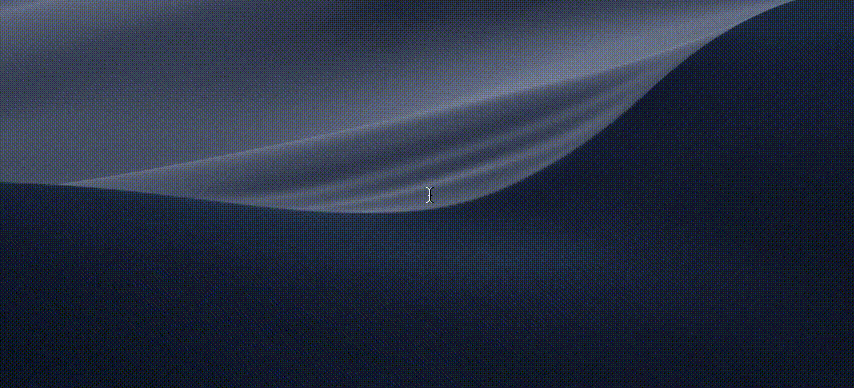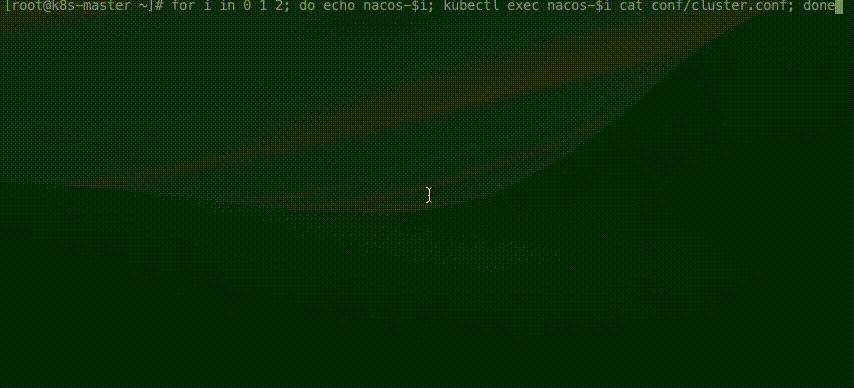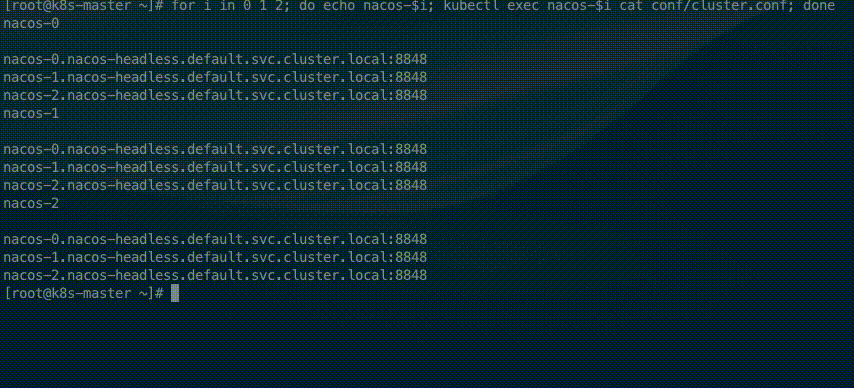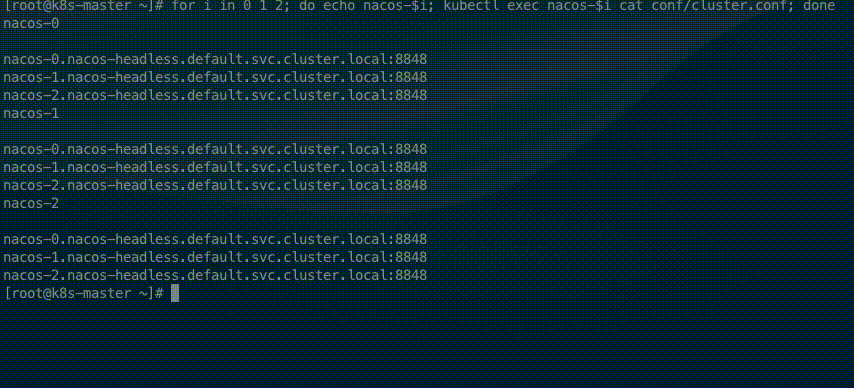
- Use
kubectl execto get the state of the Pods in thenacosStatefulSet after scale StatefulSets
for i in 0 1 2; do echo nacos-$i; kubectl exec nacos-$i curl -X GET "http://localhost:8848/nacos/v1/ns/raft/state"; doneYou can find that the new node has joined the cluster
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes Node configuration(for reference only)
| Network IP | Hostname | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| 172.17.79.3 | k8s-master | CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core) Single-core processor Mem 4G Cloud disk 40G |
| 172.17.79.4 | node01 | CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core) Single-core processor Mem 4G Cloud disk 40G |
| 172.17.79.5 | node02 | CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core) Single-core processor Mem 4G Cloud disk 40G |
- Kubernetes version:1.12.2+
- NFS version:4.1+
Limitations
- Persistent Volumes must be used. emptyDirs will possibly result in a loss of data
Project directory
| Directory Name | Description |
|---|---|
plugin | Help Nacos cluster achieve automatic scaling in K8s |
deploy | Deploy the required files |
Configuration properties
- nacos-pvc-nfs.yaml or nacos-quick-start.yaml
| Name | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
mysql.master.db.name | Y | Master database name |
mysql.master.port | N | Master database port |
mysql.slave.port | N | Slave database port |
mysql.master.user | Y | Master database username |
mysql.master.password | Y | Master database password |
NACOS_REPLICAS | Y | The number of clusters must be consistent with the value of the replicas attribute |
NACOS_SERVER_PORT | N | Nacos port,default:8848 |
PREFER_HOST_MODE | Y | Enable Nacos cluster node domain name support |
- nfs deployment.yaml
| Name | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
NFS_SERVER | Y | NFS server address |
NFS_PATH | Y | NFS server shared directory |
server | Y | NFS server address |
path | Y | NFS server shared directory |
- mysql yaml
| Name | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD | N | Root password |
MYSQL_DATABASE | Y | Database Name |
MYSQL_USER | Y | Database Username |
MYSQL_PASSWORD | Y | Database Password |
MYSQL_REPLICATION_USER | Y | Master-slave replication username |
MYSQL_REPLICATION_PASSWORD | Y | Master-slave replication password |
Nfs:server | Y | NFS server address |
Nfs:path | Y | NFS server shared path |
