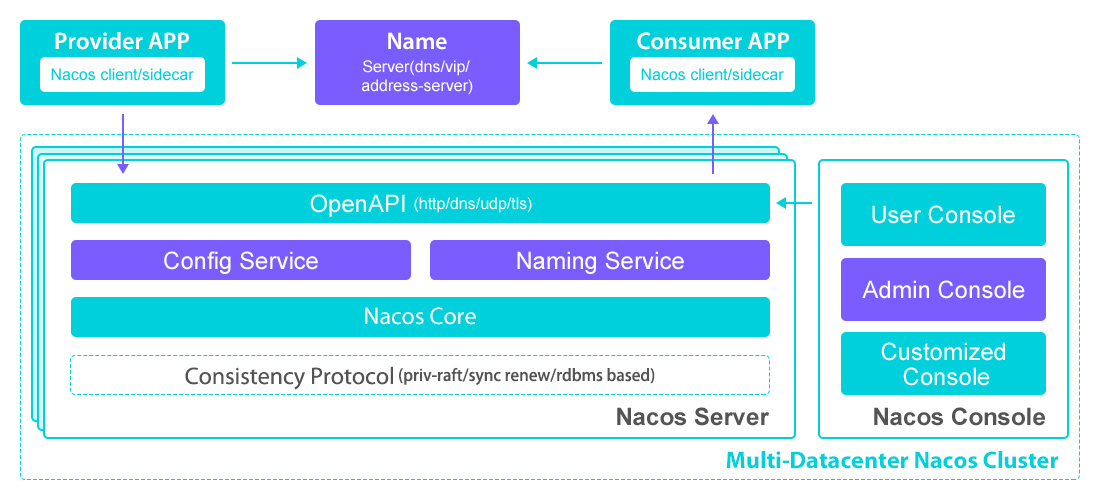
Nacos architecture
Document optimizing…
Basic Architecture and Concepts
Service
A software function or a set of software functions (such as the retrieval of specified information or the execution of a set of operations) with the purpose that different clients can be reused for different purposes (for example, through a cross-process network call). Nacos supports almost all types of services: Kubernetes Service
Service Registry
The database of services, instances and metadata. Service instances are registered with the service registry on startup and deregistered on shutdown. Clients of the service and/or routers query the service registry to find the available instances of a service. A service registry might invoke a service instances health check API to verify that it is able to handle requests.
Service Metadata
Data describing services such as service endpoints, service labels, service version, service instance weights, routing rules, security policies.
Service Provider
A process or application which provides reusable and callable services.
Service Consumer
A process or application which initiates a call to a service.
Configuration
During system development, developers usually extract some parameters or variables that need to be changed from the code and manage them in a separate configuration file. This enables the static system artifacts or deliverables (such as WAR and JAR packages) to fit with the physical operating environment in a better way. Configuration management is generally a part of system deployment, which is executed by the administrator or operation and maintenance personnel. Configuration modification is an effective method to adjust the behavior of a running system.
Configuration Management
In the data center, all configuration-related activities such as editing, storage, distribution, change management, history version management, and change audit are collectively referred to as configuration management.
Naming Service
Mapping the “names” of all the objects and entities in the distributed system to the associated metadata, for example, ServiceName -> Endpoints\Version etc..., Distributed Lock Name -> Lock Owner/Status Info, DNS Domain Name -> IP List. Service discovery and DNS are the two major scenarios of naming service.
Configuration Service
Providing dynamic configuration, service metadata and configuration management for other services or application.
More concepts…
Introduction to logical architecture and its components
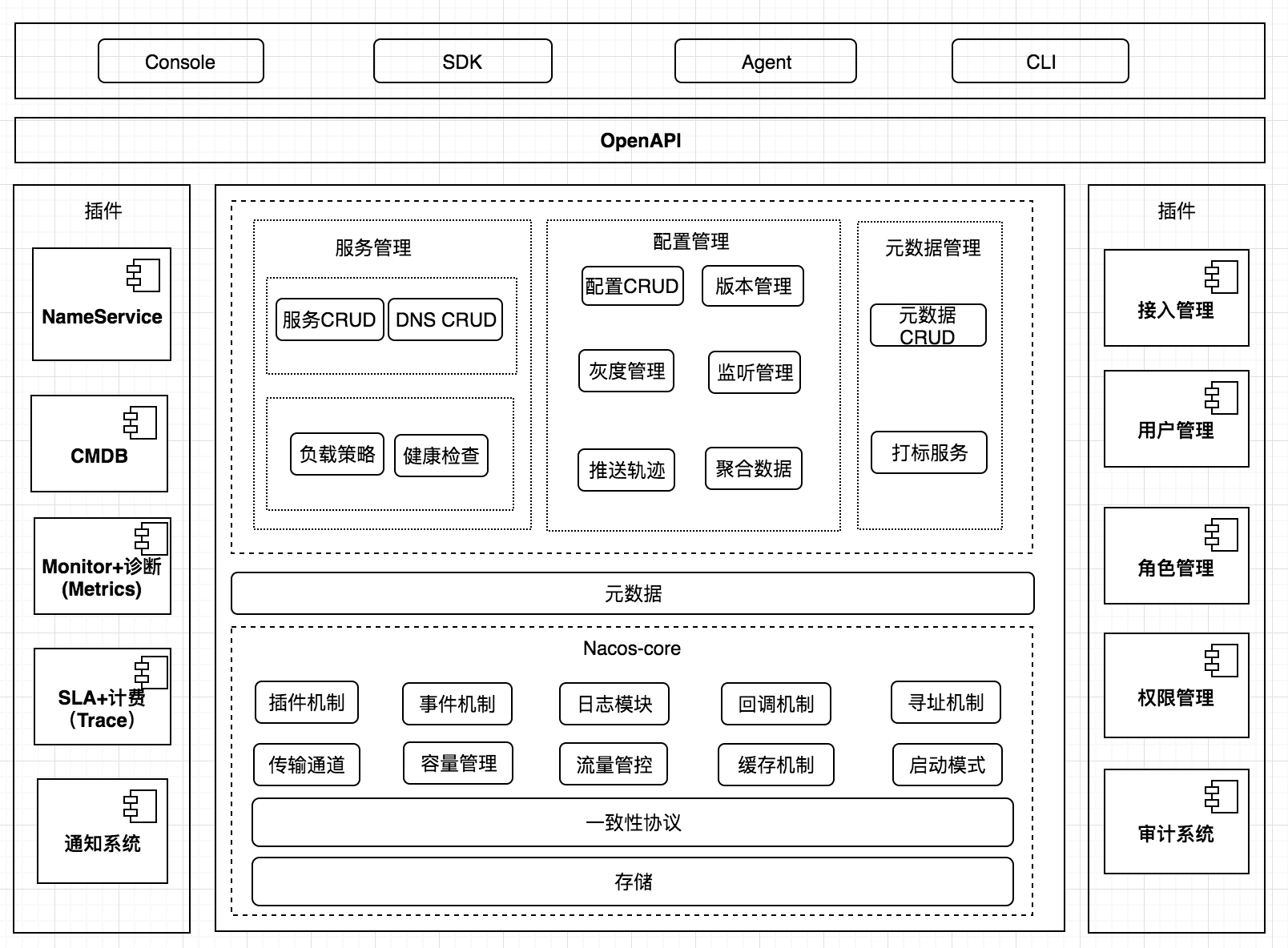
- Service Management: Implement services CRUD, domain name CRUD, service health check, service weight management, etc.
- Configuration Management: Implement configuration CRUD, version management, grayscale management, monitoring management, push trajectory, aggregate data, etc.
- Metadata Management: Provides metadata CURD and marking capabilities
- Plug-in mechanism: implements three modules to share the ability to implement the extended point SPI mechanism
- Event mechanism: implement asynchronous event notification, sdk data change asynchronous notification and other logic
- Log module: Manage log classification, log level, log portability (especially to avoid conflicts), log format, exception code + help documentation
- Callback mechanism: sdk informs the data and calls back user processing through a unified mode. Interface and data structures need to be scalable
- Addressing mode: solve various addressing modes such as ip, domain name, nameserver, broadcast, etc., need to be expandable
- Push channel: solve the push performance problem between server and storage, server, server and sdk
- Capacity management: manage each tenant, the capacity under the group, prevent the storage from being blasted, affecting service availability
- Traffic management: control the request frequency, the number of long links, the size of the message, and request flow control according to multiple dimensions such as tenant and group.
- Caching mechanism: disaster recovery directory, local cache, server cache mechanism. Disaster recovery catalogue requires tools
- Startup mode: Start different programs + UI according to stand-alone mode, configuration mode, service mode, dns mode, or all mode
- Consistency Protocol: Resolve different data, different consistency requirements, different consistency mechanisms
- Storage module: solve data persistence, non-persistent storage, solve data fragmentation problem
- Nameserver: Resolve the routing problem from namespace to clusterid, solve the mapping problem between user environment and nacos physical environment
- CMDB: Solve the metadata storage, docking problems with the three-party cmdb system, solving applications, people, resource relationships
- Metrics: Exposes standard metrics data for easy access to three-way monitoring systems
- Trace: Exposure standard trace, easy to open with SLA system, log whitening, push trajectory, etc., and can be connected with metering and billing system
- Access management: equivalent to Ali cloud service, assign identity, capacity, authority process
- User Management: Resolve issues such as user management, login, sso, etc.
- Rights Management: Resolve issues such as identity, access control, role management, etc.
- Audit system: extended interface facilitates access to different company audit systems
- Notification system: Core data changes, or operations, facilitated through the SMS system, notify the corresponding person data changes
- OpenAPI: exposes the standard Rest style HTTP interface, easy to use, and easy for multi-language integration
- Console: easy to use console, do service management, configuration management, etc.
- SDK: Multilingual sdk
- Agent: dns-f similar mode, or integration with mesh and other programs
- CLI: Lightweight management of the product on the command line, as easy as git
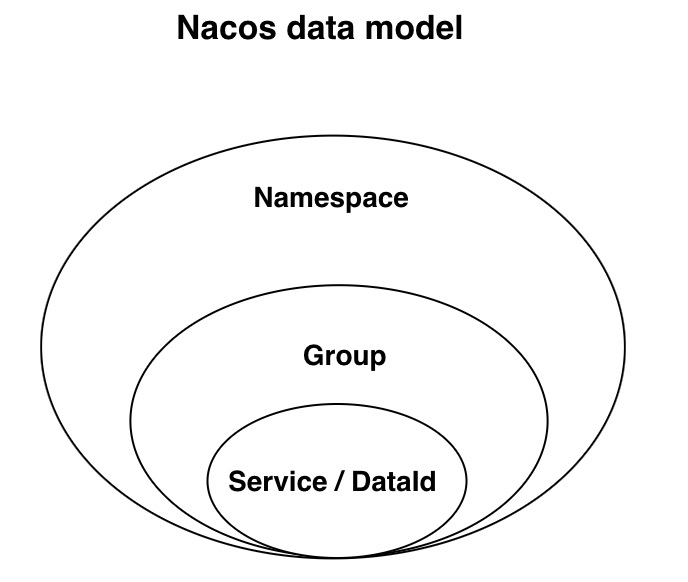
Domain Model
Data Model
The Nacos data model Key is uniquely determined by the triplet. The Namespace defaults to an empty string, the public namespace (public), and the group defaults to DEFAULT_GROUP.
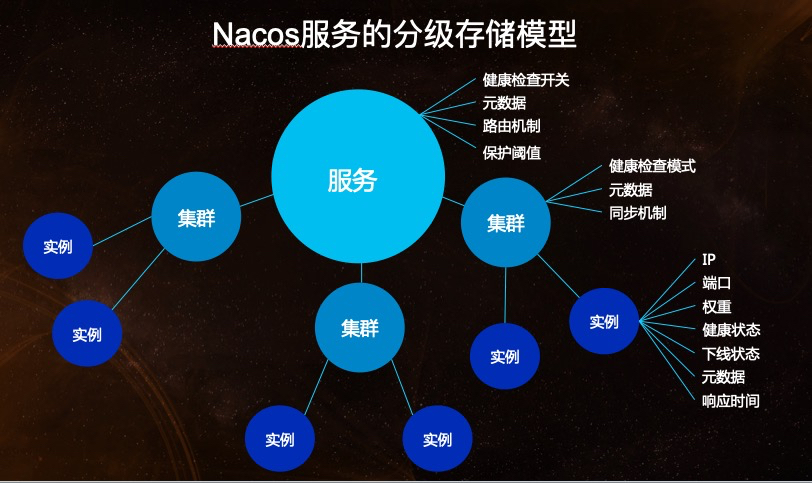
Service Entity Relationship Model
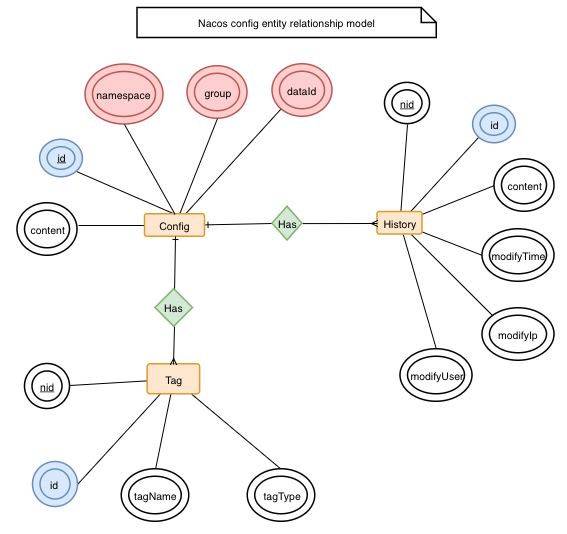
Config Entity Relationship Model
Around the configuration, there are mainly two associated entities, one is the configuration change history, and the other is the service tag (used for marking classification, convenient for indexing), which is associated by ID.
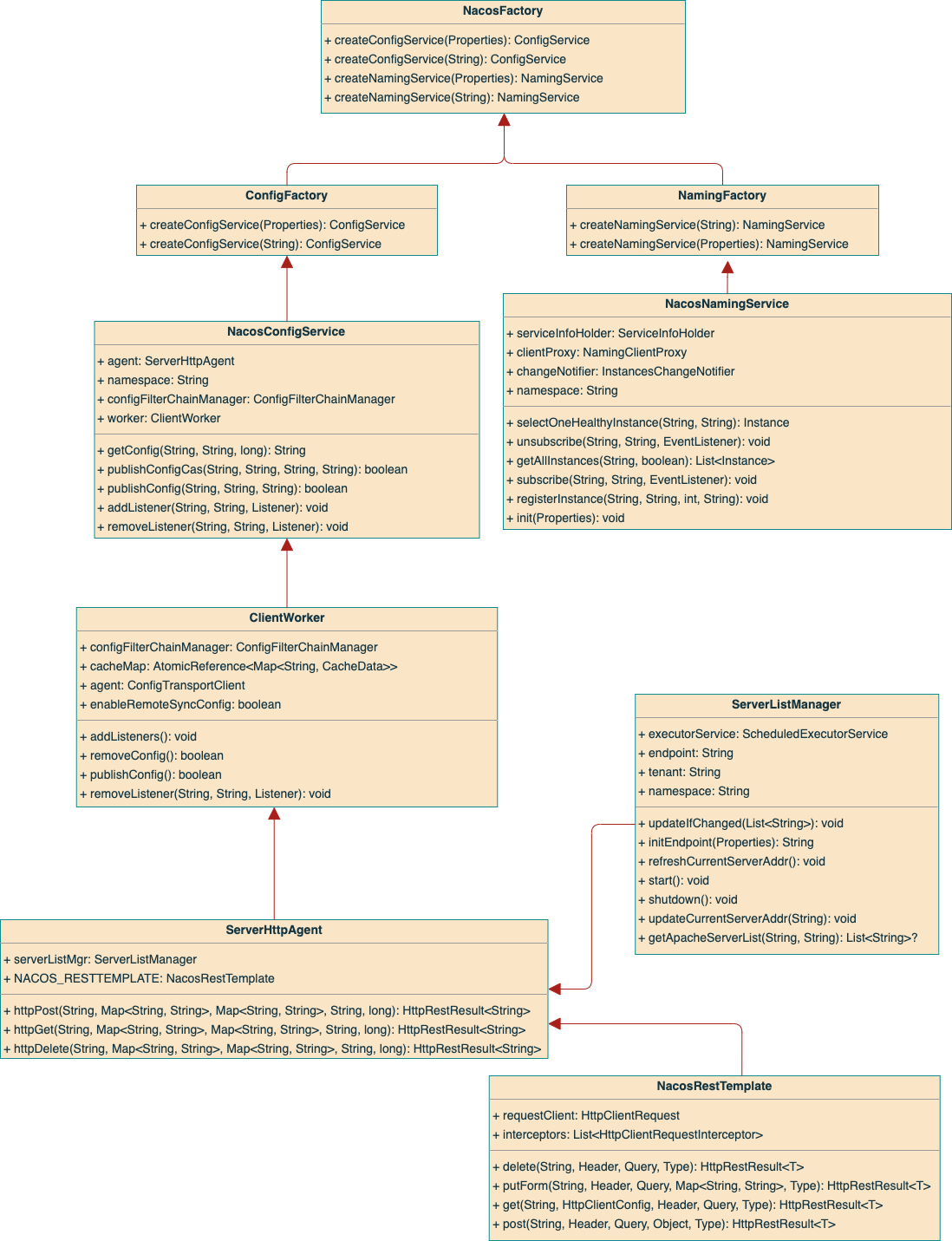
Class view
Nacos-SDK Class view
// TODO Service part to be continued
Artifacts, Deployment, and Start Mode
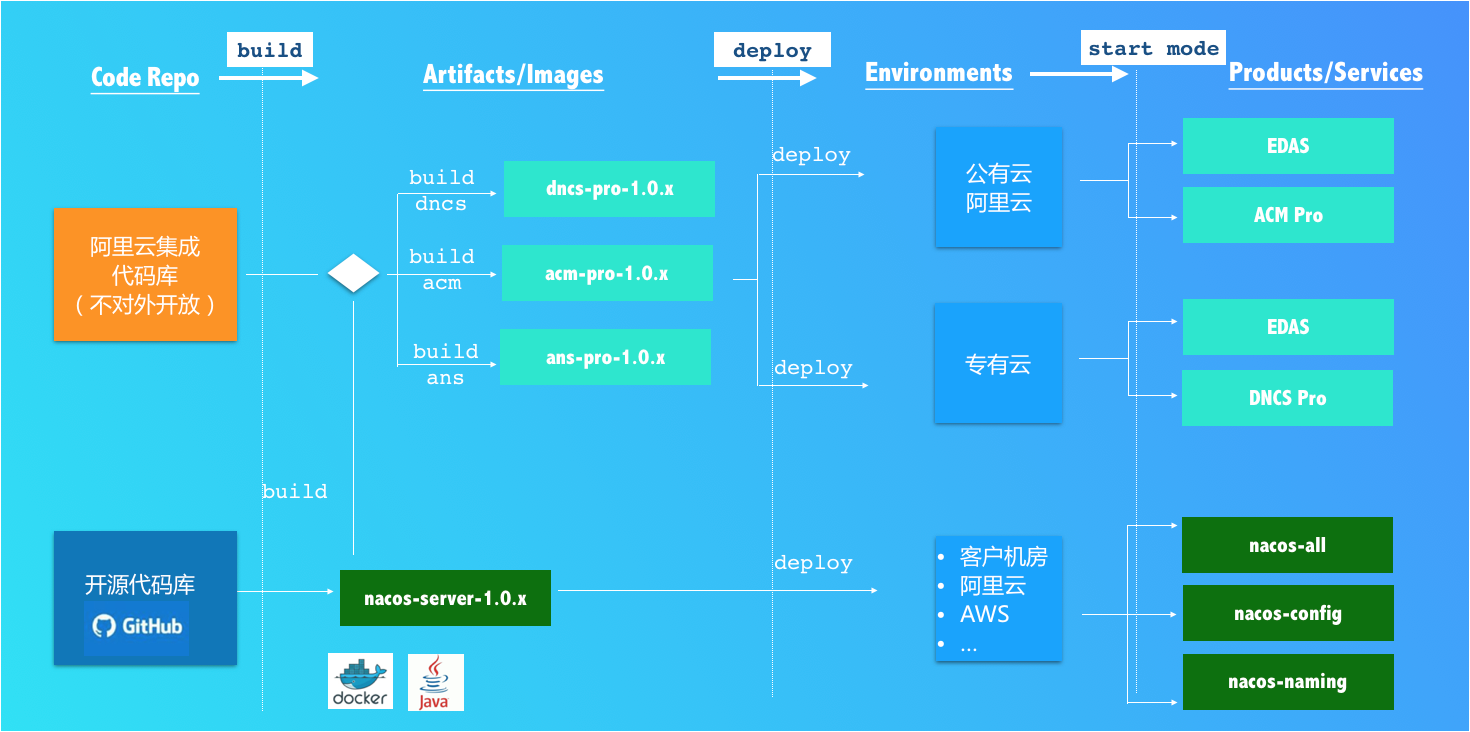
Two Artifacts
Nacos supports both standard Docker images (v0.2.0) and nacos-.zip(tar.gz). You can choose the appropriate build to deploy the Nacos service according to your needs.
Two Start Modes
Nacos supports two start modes. you can merging the Service Registry and the Config Center in one process or deploying them in separately cluster.
Free Public Cloud Service on Alibaba Cloud
In addition to deploying and launching Nacos services by users themselves, Nacos also supports public cloud. Nacos public cloud service will be free in Alibaba Cloud’s commercial service (such as MSE, EDAS). We also welcome other public cloud providers to offer Nacos public cloud services.
